Twin pregnancy refers to a pregnancy where two fetuses are developing simultaneously in the uterus, while a singleton pregnancy refers to a pregnancy with only one fetus.
Twin pregnancies can be either identical or fraternal. Identical twins develop from a single fertilized egg that splits into two, while fraternal twins develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two separate sperm

Twin pregnancies can be more challenging than singleton pregnancies, as they often involve more monitoring and care from healthcare providers. Twins may also be at a higher risk of certain complications, such as preterm birth, low birth weight, and gestational diabetes.
However, it is important to note that not all twin pregnancies are high-risk, and many twin pregnancies progress without any complications. In fact, some studies suggest that the outcomes for twins are improving as medical technology advances and healthcare providers gain more experience managing twin pregnancies.
Overall, both twin and singleton pregnancies can be healthy and successful with proper prenatal care and monitoring.
Why Twin Pregnancies Are More Challenging Than Singleton Pregnancies
Twin pregnancies can be more challenging than singleton pregnancies for a few reasons: Increased risk of complications:
- Twin pregnancies are more likely to result in complications such as preterm labor, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (a condition where blood flows unequally between the fetuses). These complications can be more difficult to manage and may require specialized care.
- There may be a greater strain on the body when carrying twins. Carrying two fetuses puts more strain on the body, as it has to work harder to provide adequate nutrition and oxygen to both babies. Pregnant individuals carrying twins may experience more fatigue, back pain, and other discomforts as a result.
- Twin pregnancy requires more frequent monitoring. Twin pregnancies often require more frequent monitoring, including more ultrasound scans and more frequent visits with healthcare providers. This is to ensure that both babies are growing and developing properly and to detect any potential complications as early as possible.
- There is a greater risk during delivery. Twin pregnancies are more likely to result in cesarean delivery, which carries its own risks and recovery time. Delivering twins vaginally can also be more challenging, as there is a higher risk of fetal distress or other complications during labor.
Risks Involved With Twin Pregnancies

Twin pregnancies are associated with a higher risk of complications compared to singleton pregnancies. Some of the common complications that can occur during a twin pregnancy include:
- Preterm labor and delivery: Twins are more likely to be born preterm, which can increase the risk of complications such as respiratory distress syndrome, bleeding in the brain, and infection.
- Growth restriction: One or both twins may not grow as expected, which can increase the risk of stillbirth, preterm delivery, and other complications.
- Preeclampsia: This condition is characterized by high blood pressure and can lead to severe complications for both the mother and babies if left untreated.
- Gestational diabetes: This condition can occur when the body is not able to produce enough insulin to control blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It can increase the risk of complications such as preterm delivery and large birth weight babies.
- Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS): This occurs when blood flows unequally between the twins and can result in serious complications for both babies.
- Cord entanglement: In some cases, the cords of the twins can become entangled, which can restrict blood flow and oxygen to one or both of the babies.
- Placental problems: The placenta(s) may not function properly, which can lead to various complications for both the mother and babies.
- Cesarean delivery: Twins are more likely to be delivered by cesarean section, which can carry its own risks and recovery time.
Cesarean Delivery vs Vaginal Delivery
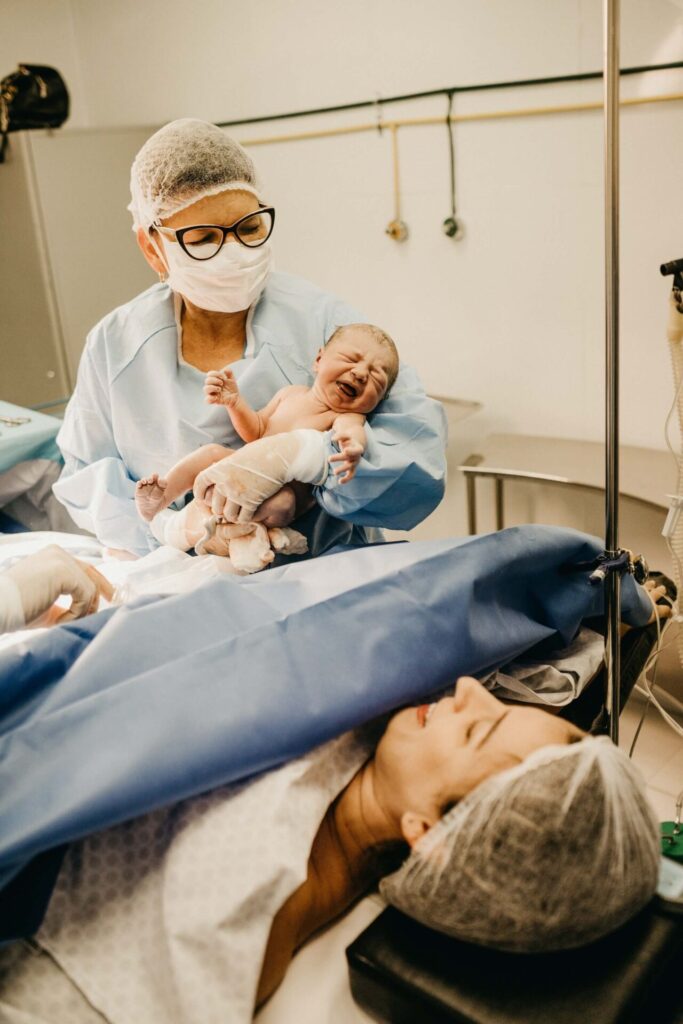

Cesarean delivery (also known as C-section) and vaginal delivery are the two main methods of giving birth. The choice of delivery method depends on various factors, such as the health of the mother and baby, the size and position of the baby, and the mother’s preferences.
A vaginal delivery involves the baby being born through the birth canal, while a C-section involves the baby being delivered through a surgical incision made in the abdomen and uterus.
Some differences between C-section and vaginal delivery include:
- Recovery time: Recovery time after a C-section is generally longer than after a vaginal delivery. C-section recovery may involve more pain, longer hospital stays, and a longer period of time before the mother can resume normal activities.
- Risk of complications: C-sections carry a higher risk of certain complications, such as infection, bleeding, and blood clots, compared to vaginal deliveries. However, vaginal deliveries carry a higher risk of certain complications, such as vaginal tears and incontinence.
- Future pregnancy: C-sections can increase the risk of complications in future pregnancies, such as placenta previa, placenta accreta, and uterine rupture. This may influence a woman’s decision about whether to have a C-section or vaginal delivery.
- Timing of delivery: In some cases, a C-section may be scheduled in advance if there are concerns about the health of the mother or baby, or if the baby is in a breech or other abnormal position. Vaginal delivery typically occurs when labor starts naturally.
It’s important to note that both C-section and vaginal delivery can be safe and successful methods of giving birth when performed under appropriate conditions and with proper medical care. The choice of delivery method should be made on an individual basis after discussing the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider.
Proper Prenatal Care And Monitoring
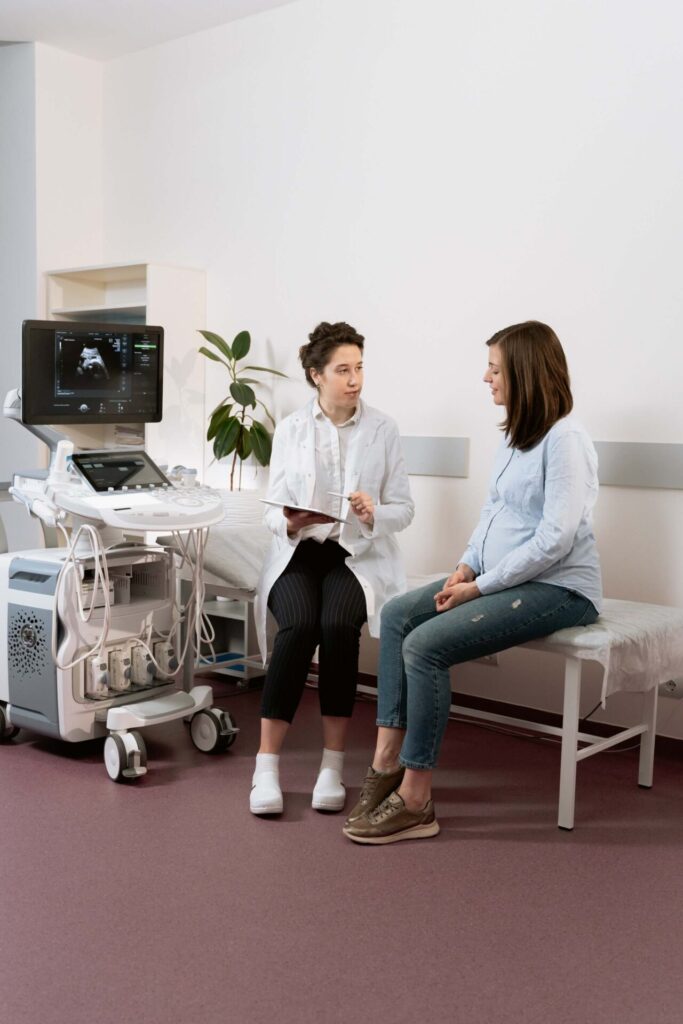

Proper prenatal care and monitoring are essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. Prenatal care involves regular check-ups with a healthcare provider throughout the pregnancy to monitor the health of the mother and the baby.
Some important aspects of prenatal care and monitoring include:
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider: Prenatal care involves regular visits with a healthcare provider to monitor the health of the mother and the baby. These visits usually occur monthly in the first trimester, every two weeks in the second trimester, and weekly in the third trimester.
- Monitoring the baby’s growth and development: Healthcare providers will use ultrasound and other tests to monitor the baby’s growth and development throughout the pregnancy.
- Monitoring the mother’s health: Prenatal care also involves monitoring the mother’s health, including blood pressure, weight, and any symptoms that may indicate a problem.
- Nutrition and lifestyle advice: Healthcare providers will provide advice on proper nutrition and lifestyle habits, such as avoiding smoking and alcohol, that can affect the health of the mother and the baby.
- Screening for health conditions: Prenatal care also involves screening for health conditions that may affect the mother or the baby, such as gestational diabetes or preeclampsia.
Proper Postnatal Care And Monitoring
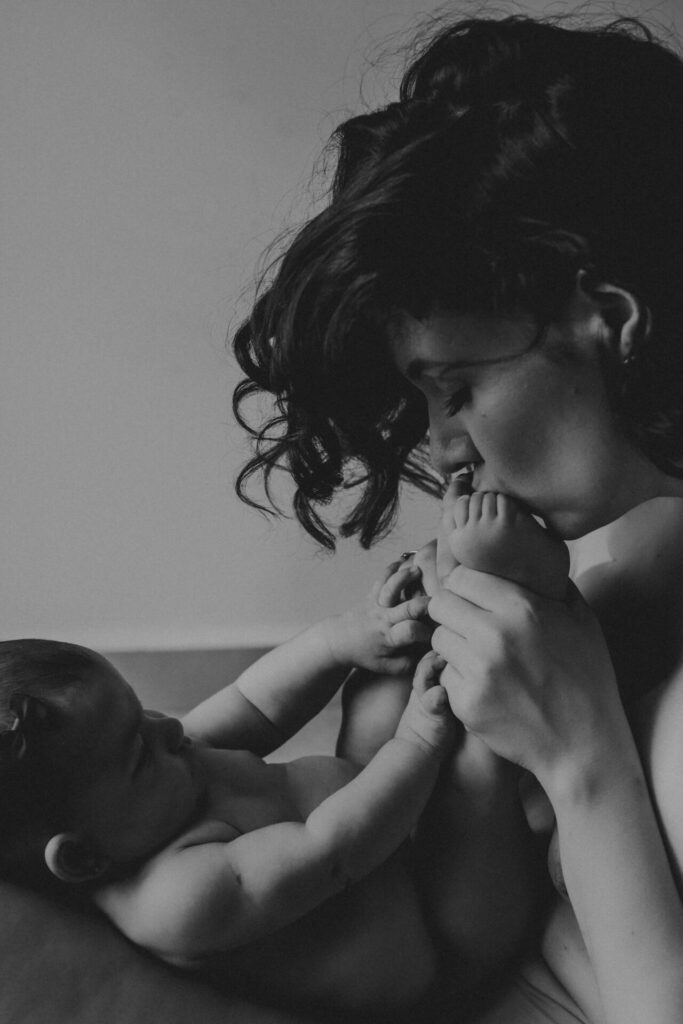

Proper postnatal care and monitoring are essential for the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby after childbirth. Postnatal care involves regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor the physical and emotional health of the mother and the baby.
Some important aspects of postnatal care and monitoring include:
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider: New mothers and babies should have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider in the first few weeks after birth to monitor their health and recovery.
- Monitoring the baby’s growth and development: Healthcare providers will monitor the baby’s growth and development, including weight gain, feeding, and any signs of health problems.
- Monitoring the mother’s recovery: Healthcare providers will monitor the mother’s physical recovery after childbirth, including any postpartum complications and emotional well-being.
- Breastfeeding support: Healthcare providers will provide support and guidance for new mothers who are breastfeeding their babies, including advice on proper positioning, latch, and milk supply.
- Contraception counseling: Healthcare providers will provide counseling on contraception options for new mothers who want to prevent another pregnancy.
- Mental health support: Healthcare providers will monitor the mental health of new mothers and provide support and referrals for postpartum depression or other mental health concerns.
Conclusion

In conclusion, twin pregnancy and singleton pregnancy have significant differences that can affect the health and well-being of both the mother and the babies. Twin pregnancies are associated with increased risks of complications such as premature birth, low birth weight, and gestational diabetes, among others.
Additionally, twin pregnancies require more intensive prenatal care and monitoring to ensure the health of both babies. On the other hand, singleton pregnancies have a lower risk of complications and may not require as much monitoring or medical intervention.
While twin pregnancies can present unique challenges, with proper prenatal care and monitoring, most twin pregnancies can result in healthy babies and mothers.
It is important for women who are pregnant with twins or a single baby to discuss their individual risks and options with their healthcare provider and follow their advice for a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Ultimately, regardless of the type of pregnancy, every mother and baby deserve the best possible care and attention to ensure a safe and healthy outcome.